The recent release of Microsoft HoloLens 2 Research Mode enriches the immersive mixed reality experience with access to IMU sensor data and articulated hand-tracking and eye-tracking capabilities. Valorem's Director of Global Innovation, Research & Incubation explains how these advantages have made HoloLens 2 an industry leader in computer vision research devices.
The HoloLens 2 is by far the most sophisticated Spatial Computing device on the market. A powerful mobile device, packed with sensors and advanced AI computer vision algorithms that can spatially process the world around us in real-time, fully untethered.
The HoloLens 2 built-in computer vision algorithms like the 3D reconstruction / spatial mapping, articulated hand tracking and more are optimized for the HoloLens’ holographic processing unit (HPU). Extending those was not possible by default, but thanks to the newly added Research Mode feature it is now possible to access the raw sensor data also on the HoloLens 2. This enables custom computer vision algorithm development with processing on the HoloLens itself, remotely on a PC or in the cloud.
Features of the Microsoft HoloLens Research Mode
Research Mode was available on the HoloLens 1 but was more limited than the new HoloLens 2 version. Combined with the latest and greatest sensor and processing units, HoloLens 2 is enabling unparalleled and powerful immersive mixed reality experiences for custom computer vision solutions.
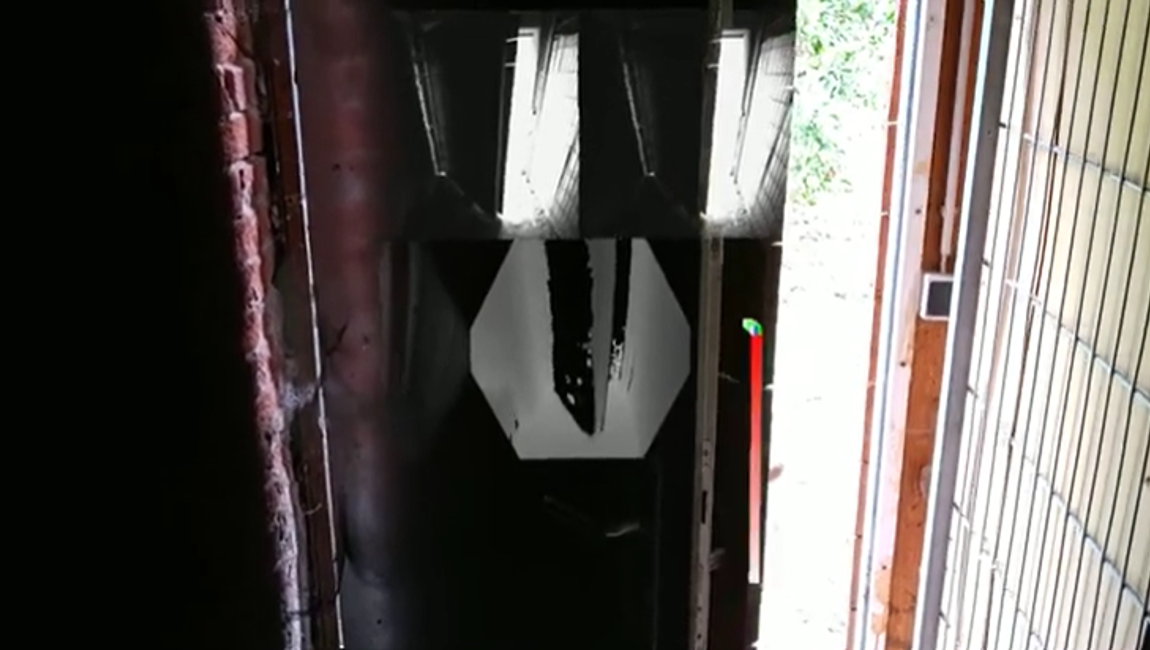
 Figure 1: HoloLens 2 built-in camera sensors accessible via Research Mode
Figure 1: HoloLens 2 built-in camera sensors accessible via Research Mode
Using Research Mode in HoloLens 2, you can enhance the immersive experience with access the following sensor data:
Visible Light Environment Tracking cameras: 4 grayscale cameras used by the system for head tracking and map building. Two of the grayscale cameras are configured as a stereo rig, capturing the area in front of the device so that the absolute depth of tracked visual features can be determined. Two additional grayscale cameras angled at the side provide a wider, better feature tracking. The cameras are synchronized with global-shutter and are more sensitive to light than the color camera, capturing images at a rate of up to 30 fps.
Depth camera: 1 Time-of-Flight / active infrared illumination camera to determine depth. This ToF camera is similar to the depth camera of the Azure Kinect, where the HoloLens 2 depth camera supports two operation modes:
- High-framerate (45 fps) near-depth sensing commonly used for hand tracking. Gives pseudo-depth with phase wrap beyond 1 meter. For example objects at 1.5m distance will be reported at 0.5m distance and so on.
- Low-framerate (1-5 fps) far-depth sensing, currently used by spatial mapping.
In both modes the depth camera also provides actively illuminated infrared (IR) images which are mostly unaffected by ambient light and can be useful on their own.
Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) / motion sensor consisting of:
- Accelerometer used by the system to determine linear acceleration along the X, Y and Z axes and gravity.
- Gyro used by the system to determine rotations.
- Magnetometer used by the system to estimate absolute orientation.
RGB color camera: This is the default color camera used for Mixed Reality Captures and can also be accessed without Research Mode enabled via various APIs like Windows.MediaCapture or Unity. It is an auto-focus photo/video camera with auto white balance, auto exposure, and full image processing pipeline. It has various modes of operation, ranging from high resolution and 60 fps to more lower resolution camera profiles. The full list is available here.
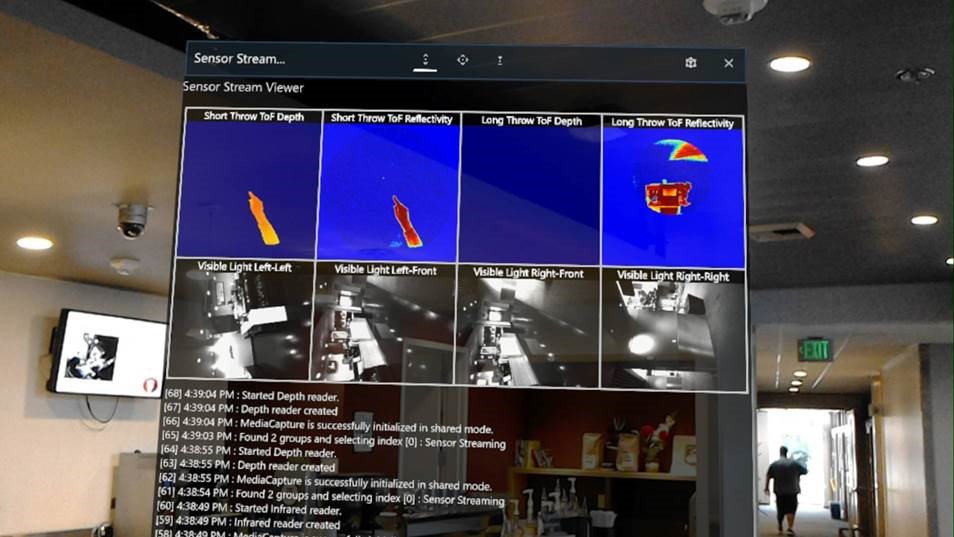 Figure 2: Screenshot of a test app visualizing all sensor streams on the HoloLens
Figure 2: Screenshot of a test app visualizing all sensor streams on the HoloLens
The HoloLens 2 Research Mode allows applications to also simultaneously leverage the results of the built-in computer vision, such as SLAM, for motion tracking of the device as well as the spatial mapping algorithms for environmental 3D reconstruction, articulated hand-tracking and eye tracking. Access to the raw eye tracking cameras is not provided for privacy and security reasons but existing APIs can access the processed eye-gaze direction.
Setting Up HoloLens 2 Research Mode
HoloLens 2 Research Mode is available as a public preview beginning with Windows build 19041.1356- which is provided via the Insider Preview program at the moment- and will be available as a regular update in the future. Be aware that enabling Research Mode uses more battery power and can also lower the overall security of the device due to application sensor data misuse, therefore make sure to only run trusted applications leveraging Research Mode APIs.
Once the correct Windows build is running on the HoloLens, the Research Mode needs to be enabled via the Device Portal by checking “Allow access to sensor streams” and rebooting the device:
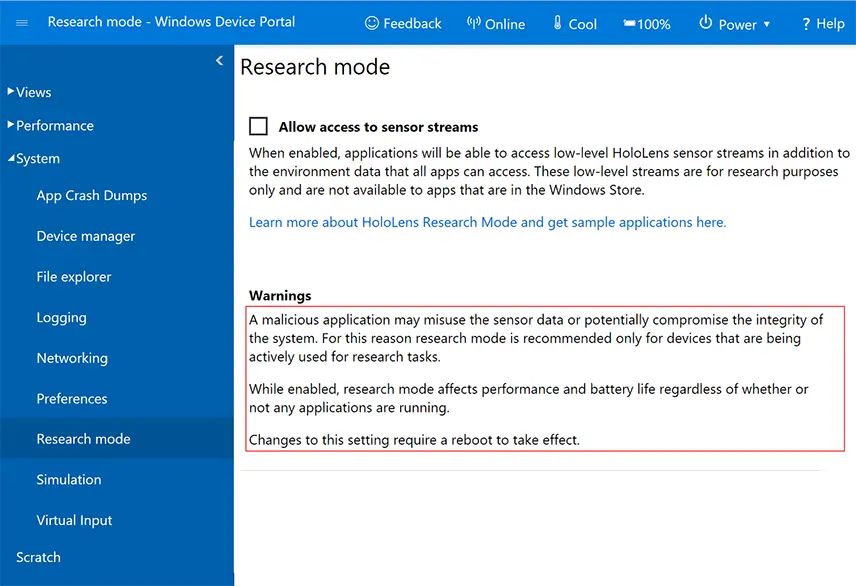 Figure 3: Research Mode page in the HoloLens Windows Device Portal
Figure 3: Research Mode page in the HoloLens Windows Device Portal
Research Mode’s Built-In Sensor Streams
The various sensor streams can be accessed via Microsoft’s Media Foundation API layer. To get started it’s best to use one of the four samples developed by Microsoft’s Mixed Reality research team released as open source on GitHub:
- SensorVisualization: visualizes camera streams live on the HoloLens device.
- CalibrationVisualization: visualizes depth and gray-scale camera coordinate frames live.
- CameraWithCVAndCalibration: shows how to process Research Mode streams live on the HoloLens 2, leveraging the popular computer vision library OpenCV to detect arUco markers in the two frontal gray-scale cameras and triangulate the detections.
- StreamRecorder: simultaneously captures depth, gray-scale cameras, head, hand, and eye tracking data and saves the streams on the HoloLens device. Additionally, Python scripts are provided for offline processing of the recorded streams on a PC or in the cloud.
In the below video I walk-through the SensorVisualization sample and show how to use it end-to-end, including a use case allowing night vision!
Modernizing Your Workplace with HoloLens 2 and Research Mode
The HoloLens 2 Research Mode allows us to research custom computer vision solutions for specialized use cases and is not aimed for end-user deployments. We at Valorem Reply are here to help with our experienced team of computer vision and HoloLens developers, artists, and designers. If you have a Spatial Computing project in mind (with or without Research Mode), we would love to hear about it! Reach out to us as marketing@valorem.com to schedule time with one of our industry experts.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is HoloLens 2 Research Mode and why is it significant?
HoloLens 2 Research Mode provides access to raw sensor data including IMU, hand-tracking, and eye-tracking capabilities, enabling custom computer vision algorithm development for advanced mixed reality experiences.
How many visible-light environment tracking cameras does HoloLens 2 have?
HoloLens 2 includes four grayscale cameras—two configured as stereo rigs capturing frontal areas, two positioned at angles providing wider feature tracking, synchronized with global-shutter at thirty frames per second.
What depth-sensing modes does the HoloLens 2 ToF camera support?
The Time-of-Flight depth camera supports high-framerate forty-five fps near-depth sensing for hand tracking and low-framerate one-to-five fps far-depth sensing for spatial mapping operations.
Which sensor components comprise the HoloLens 2 IMU/motion sensor?
The IMU consists of an accelerometer determining linear acceleration along X, Y, Z axes and gravity, gyro measuring rotations, and magnetometer estimating absolute device orientation.
What RGB color camera capabilities does HoloLens 2 provide?
HoloLens 2 includes an auto-focus RGB camera with auto white balance, auto exposure, and full image processing pipeline, supporting various modes from high resolution to lower resolution profiles.
How is HoloLens 2 eye-tracking data accessed through Research Mode?
Raw eye-tracking camera data access is restricted for privacy and security reasons, but existing APIs provide processed eye-gaze direction information for authorized applications.
What Windows build version enables HoloLens 2 Research Mode?
Research Mode is available starting with Windows build nineteen thousand forty-one point one thousand three hundred fifty-six via the Insider Preview program, with future regular updates planned.
How is Research Mode enabled on HoloLens 2?
Research Mode is enabled through the Device Portal by checking "Allow access to sensor streams" and rebooting the device after correct Windows build installation.
What are the four Microsoft-provided open-source Research Mode samples?
Microsoft provides SensorVisualization, CalibrationVisualization, CameraWithCVAndCalibration using OpenCV, and StreamRecorder for capturing and offline processing sensor streams simultaneously.
What security considerations exist when enabling HoloLens 2 Research Mode?
Enabling Research Mode increases battery consumption and reduces device security due to potential application sensor data misuse, requiring only trusted applications to be run.
Can Research Mode processing occur remotely or in the cloud?
Yes. Custom computer vision algorithms can process Research Mode data on HoloLens itself, remotely on a PC, or in cloud environments, providing flexible deployment options.
What specialized use cases does HoloLens 2 Research Mode support?
Research Mode enables custom computer vision solutions including night vision capabilities, marker detection, environmental 3D reconstruction, and specialized spatial computing applications.
Which computer vision library integrates with HoloLens 2 Research Mode?
The CameraWithCVAndCalibration sample demonstrates OpenCV integration for detecting ArUco markers in frontal grayscale cameras and triangulating detection results on HoloLens 2.
Can Research Mode access built-in HoloLens 2 computer vision results?
Yes. Applications can simultaneously leverage built-in computer vision results including SLAM motion tracking, spatial mapping algorithms, hand-tracking, and eye-tracking capabilities.








